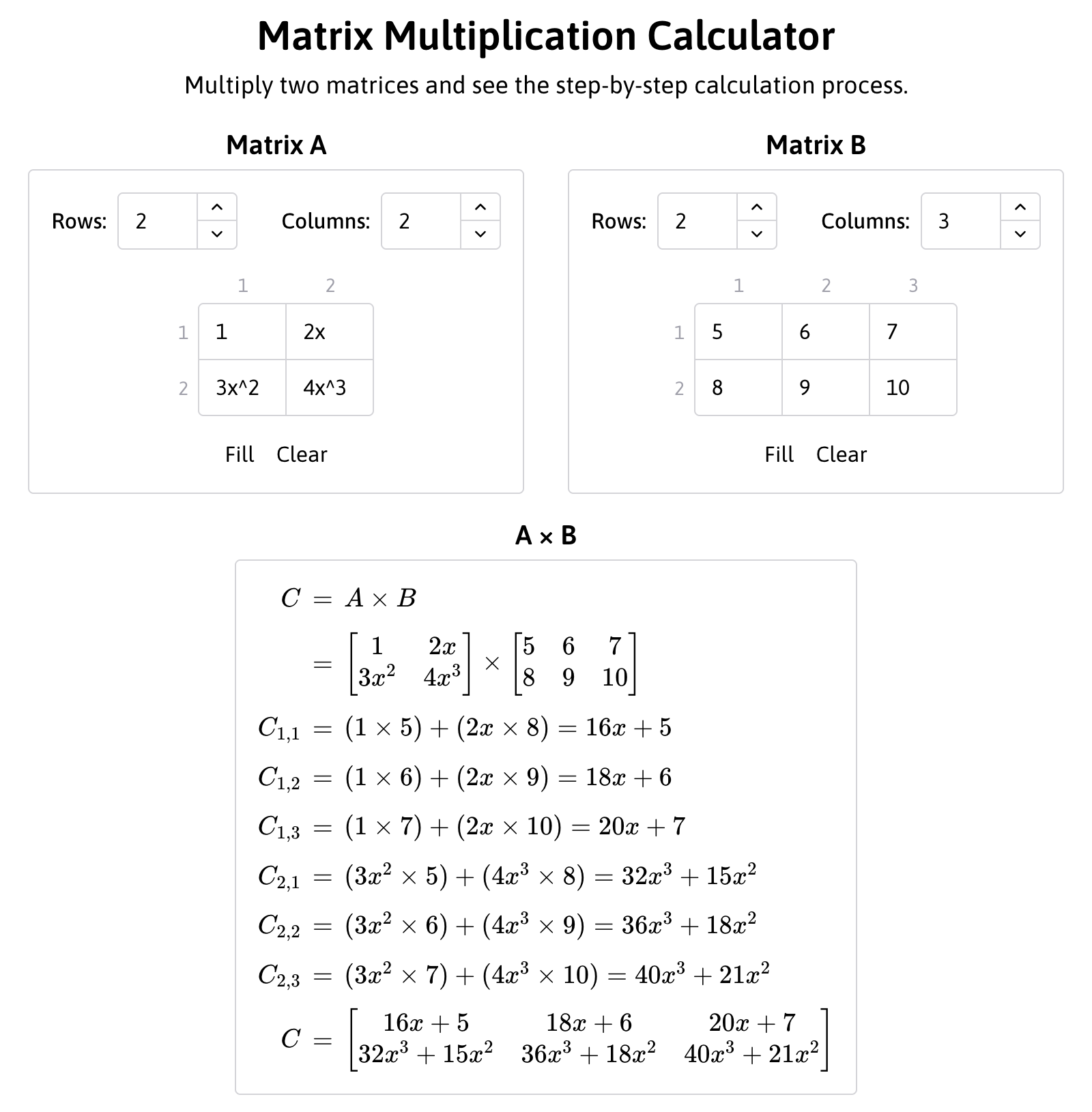
Matrix Multiplication Calculator
Multiply two matrices and see the step-by-step calculation process.
Matrix Multiplication Calculator Features
- Algebraic Expression Support: Enter variables and algebraic expressions (like or ) directly in matrix cells to perform symbolic multiplication.
- Step-by-Step Calculation: View the complete calculation process for each element in the resulting matrix, showing exactly how each value is computed.
- Dynamic Matrix Sizing: Adjust matrix dimensions on the fly to work with matrices of any compatible size.
- Interactive Highlighting: Click on any matrix cell to see which elements are used in the calculation, highlighted in bold throughout the step-by-step breakdown.
- Automatic Simplification: The calculator automatically simplifies algebraic expressions in the results, making complex calculations easier to understand.
What is Matrix Multiplication?
Matrix multiplication is a binary operation that produces a matrix from two matrices. For matrices and , the product is defined only when the number of columns in equals the number of rows in .
If is an matrix and is an matrix, then their product will be an matrix.
How Does it Work?
Each element in the resulting matrix is computed by taking the dot product of the corresponding row from the first matrix and column from the second matrix.
- Matrix of size and Matrix of size .
- is the row index () and is the column index ().
Key Properties
Matrix multiplication has several important properties, some of them being different from regular number multiplication:
- Non-Commutative: In general, . The order of multiplication matters and changing it usually produces different results.
- Associative: . You can regroup matrix multiplications without changing the result.
- Distributive: and . Matrix multiplication distributes over addition.
- Identity Element: Multiplying by an identity matrix leaves the matrix unchanged: .
Common Examples
Identity Matrix
An identity matrix has ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. Multiplying any matrix by an appropriately sized identity matrix returns the original matrix:
Scalar Multiplication
When you multiply a scalar (regular number) by a matrix, it multiplies every element in the matrix. For example:
Screenshot
Here is a screenshot of the calculator in action: